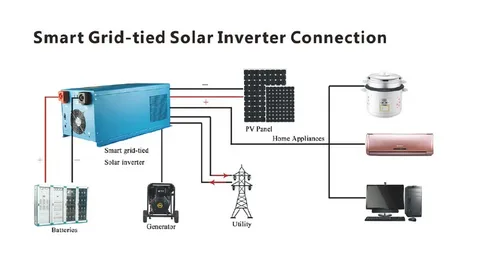
Solar power systems are one of the most efficient and environmentally friendly ways to generate electricity. Solar inverters, however, are often overlooked as a crucial component in any solar power system. This article will discuss what an inverter is, how they work and how you can choose the best solar inverter for your needs.
Solar Inverters Are The Heart Of The Solar Power System
Solar inverters are the heart of the solar power system. They convert DC voltage from your solar panels into AC voltage, which is used to power your home or business. This process is crucial in any solar energy system and can be thought of as similar to how a car battery works–it’s what allows you to use electricity stored in one place (like your car) at another location (like your home). Without an inverter, there would be no way for you to access that stored energy!
To maximize efficiency and reduce costs in these systems, it’s essential for homeowners and businesses alike not only to choose the right size but also to ensure they purchase high-quality equipment with low failure rates over time so that their investment lasts as long as possible without needing repairs or replacements due out-of-pocket expenses down the road.”
A Solar Inverter Changes DC (Direct Current) Voltage To AC (Alternating Current)
Inverters are a crucial component in any solar power system. They convert energy from the sun into AC, which can be used to power appliances and devices. The solar inverter is usually the most expensive component in a solar power system, so choosing one with high efficiency and long life expectancy is essential.
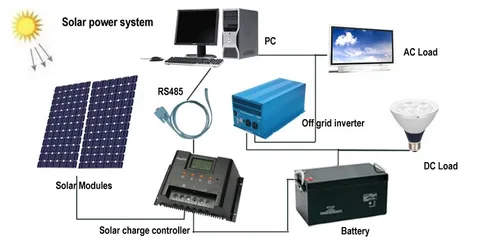
There are two types of solar inverters: grid-tied and off-grid. Grid-tied inverters are connected to the utility grid, which allows you to sell back any extra energy you generate from your solar panels. Off-grid inverters don’t connect to the utility grid, so all power generated by your system is used onsite.
The Role Of An Inverter Is To Convert The Energy Stored In Batteries Into AC
An inverter is a device that converts DC (direct current) into AC (alternating current). It means it takes energy from your solar panels and batteries and converts it into household AC power.
The role of an inverter is to convert the direct current produced by your solar panels into alternating current, which can be used by appliances in your home. A good quality inverter will also protect against overcharging and overloading and provide support for maintenance-free operation with no moving parts to wear out or replace.
When choosing an inverter, consider your budget and how much power your home uses. The higher the wattage of your solar panels, the more power you can store in batteries and use at night or on cloudy days.
A Solar Power Inverter Is A Crucial Component In Any Solar Power System
A solar power inverter is a crucial component in any solar power system. The inverter converts DC energy stored in batteries into AC, then fed to your home’s electrical panel and other appliances. Inverters are the heart of the system, so choosing one with good-quality components that will last many years is essential.
An inverter is the heart of a solar power system. It converts DC energy stored in batteries into AC, then fed to your home’s electrical panel and other appliances. Inverters are the heart of the system, so choosing one with good-quality components that will last many years is essential.
There are many different types of inverters available on the market today. The most common are grid-tied and off-grid inverters, but there are also pure sine-wave and modified sine-wave models. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, grid-tied systems allow you to take advantage of net metering credits or feed excess power back into the grid, while off-grid systems don’t require any connection to an external power source.
There Are Two Types Of Solar Inverters – String And Microinverters
There are two types of solar inverters: string and microinverters. String inverters are connected in series, while microinverters are connected in parallel.
Microinverters have become more popular over the past few years due to their efficiency and reliability, but they require more space than a string inverter. String inverters are cheaper than microinverters, but they’re less efficient and unreliable if you don’t know what you’re doing when installing them on your roof or wall (or wherever else).
The main difference between string inverters and microinverters is that the latter can be installed on individual solar panels, while string inverters must be connected to multiple panels in series.
It means that microinverters are more efficient and reliable than string inverters. They also require less space on your roof or wall, which is essential if you don’t have a lot of room to install solar panels.
Solar Inverters Are One Of The Most Essential Equipment In A Solar Power System
Solar inverters are one of the most essential equipment in a solar power system. They convert DC power from your solar panels into usable AC power for your home or business. The heart of your system, they’re responsible for converting the energy from those shiny photovoltaic cells on your roof into usable electricity for you to use when you need it most–whether that’s during an evening at home watching Netflix or powering up tools at work before heading out to start another day.
A quality inverter can handle whatever load you throw at it: running several high-wattage appliances simultaneously or just keeping some lights on while reading a book after dark (or both).
Inverters can be found in almost any type of solar power system, whether a small residential set-up or a large commercial installation.
 While Both Types Have Advantages And Disadvantages, Micro-Inverters Are Usually The Better Option
While Both Types Have Advantages And Disadvantages, Micro-Inverters Are Usually The Better Option
While both types have advantages and disadvantages, micro-inverters are usually the better option. Here’s why:
They’re more efficient: Microinverters send power directly to each solar panel instead of routing it through a string of panels. It allows for a more direct path from sun to electricity, which means you get more out of your investment in solar panels.
They’re more reliable: Microinverters don’t have any moving parts, so nothing can break down or wear out over time like there would be with traditional string inverters (which use moving magnets). Plus, microinverters are less likely to fail because they don’t require any additional equipment besides what comes standard on each panel itself–and if one fails? You replace it!
They’re easier to install: Since each panel has its microinverter attached directly to its frame, there’s no need for complex wiring schemes like those required by traditional string inverters–you plug them into an outdoor junction box and voila! You’ve got some clean energy without all those messy wires running everywhere. Not only does this mean less work during installation, but also less maintenance afterwards!
How To Choose An Off Grid Solar Inverter?
The size of your solar system will determine the peak wattage of your inverter. The larger the size of your system, the more power it can produce and store. If you have a large system, consider choosing an inverter with a higher wattage capacity than one suitable for smaller systems.
A high-reliability factor is also essential when choosing an off grid solar inverter because these devices are responsible for converting DC current from batteries into AC current that can be used inside homes or businesses. If there’s any interruption in this conversion process due to malfunctioning components within an inverter unit itself (such as diodes), then there could potentially be serious consequences such as battery damage or fire hazards if left unchecked over time – which could easily lead up costing thousands upon thousands of worth dollars in repairs later down the line!
When Choosing An Off Grid Inverter, Factors Include Solar System Size, Peak Wattage And Reliability
When choosing an off grid inverter, you should consider the following factors:
Solar System Size
The size of your solar system will determine how much power it can generate at any given time. An extensive system with high wattage requires a corresponding inverter capable of handling this load. For example, suppose you have a 1000W solar panel and use it with another 1000W panel or two 500W panels.
In that case, you will need an inverter rated for at least 2000W or 2500W, respectively (the exact amount depends on whether they operate together). You should also consider whether or not any other appliances will be connected to this particular set-up and how many hours per day these appliances will be used before deciding which kind of inverter best suits your needs.
Peak Wattage/Voltage Rating
This refers to how much energy can be stored at any given time before overloading occurs.
System Frequency
Different countries operate their electricity grids at different frequencies; therefore, it is essential for any good alternative energy solution provider who installs such systems to know exactly what frequency transfer capabilities are needed before purchasing one.
System Temperature Range Limits
If temperatures rise above 45 degrees Celsius during summer months when air conditioning units are being used frequently, then there could be severe consequences such as overheating, which could lead to complete failure if left unchecked long enough
Conclusion
Choosing the suitable inverter is crucial if you’re looking to maximize your solar efficiency and get the most bang out of every watt. This article covers what you need to know about solar inverters and how they work. We’ve also given some tips on choosing an off-grid inverter that will work best for your home or business!